Publications
Note: * denotes equal contribution; † denotes project leader or corresponding author.
Full list on Google Scholar
2025
-
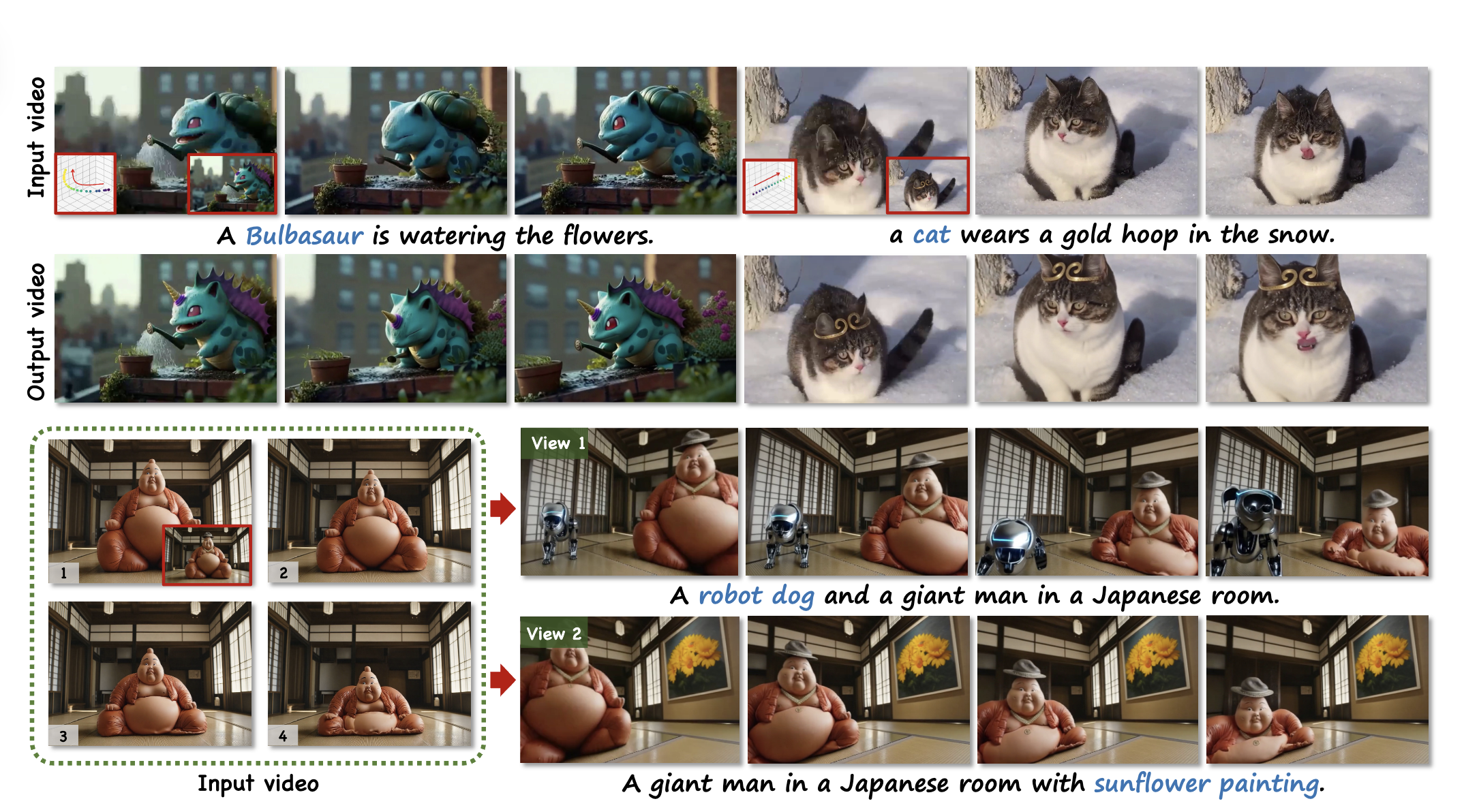 Follow-Your-Creation: Empowering 4D Creation through Video InpaintingYue Ma*, Yukun Feng*, Xinhua Zhang*, Hongyu Liu†, Junhao David Zhang, and 5 more authorsarXiv preprint arXiv:2506.04590, 2025
Follow-Your-Creation: Empowering 4D Creation through Video InpaintingYue Ma*, Yukun Feng*, Xinhua Zhang*, Hongyu Liu†, Junhao David Zhang, and 5 more authorsarXiv preprint arXiv:2506.04590, 2025We introduce Follow-Your-Creation, a novel 4D video creation framework capable of both generating and editing 4D content from a single monocular video input; by leveraging a powerful video inpainting foundation model as a generative prior, we reformulate 4D video creation as a video inpainting task, enabling the model to fill in missing content caused by camera trajectory changes or user edits; to facilitate this, we generate composite masked inpainting video data to effectively fine-tune the model for 4D video generation; given an input video and its associated camera trajectory, we first perform depth-based point cloud rendering to obtain invisibility masks that indicate the regions that should be completed; simultaneously, editing masks are introduced to specify user-defined modifications, and these are combined with the invisibility masks to create a composite masks dataset; during training, we randomly sample different types of masks to construct diverse and challenging inpainting scenarios, enhancing the model’s generalization and robustness in various 4D editing and generation tasks; to handle temporal consistency under large camera motion, we design a self-iterative tuning strategy that gradually increases the viewing angles during training, where the model is used to generate the next-stage training data after each fine-tuning iteration; moreover, we introduce a temporal packaging module during inference to enhance generation quality; our method effectively leverages the prior knowledge of the base model without degrading its original performance, enabling the generation of 4D videos with consistent multiview coherence; in addition, our approach supports prompt-based content editing, demonstrating strong flexibility and significantly outperforming state-of-the-art methods in both quality and versatility.
@article{ma2025followcreation, title = {Follow-Your-Creation: Empowering 4D Creation through Video Inpainting}, author = {Ma, Yue and Feng, Yukun and Zhang, Xinhua and Liu, Hongyu and Zhang, Junhao David and Xing, Jinbo and Zhang, Yinhan and Yang, Ayden and Wang, Zeyu and Chen, Qifeng}, journal = {arXiv preprint arXiv:2506.04590}, year = {2025}, } -
 Follow-Your-Emoji-Faster: Towards Efficient, Fine-Controllable, and Expressive Freestyle Portrait AnimationYue Ma*, Zexuan Yan*, Hongyu Liu*, Hongfa Wang, Heng Pan, and 9 more authorsInternational Journal of Computer Vision (IJCV), 2025
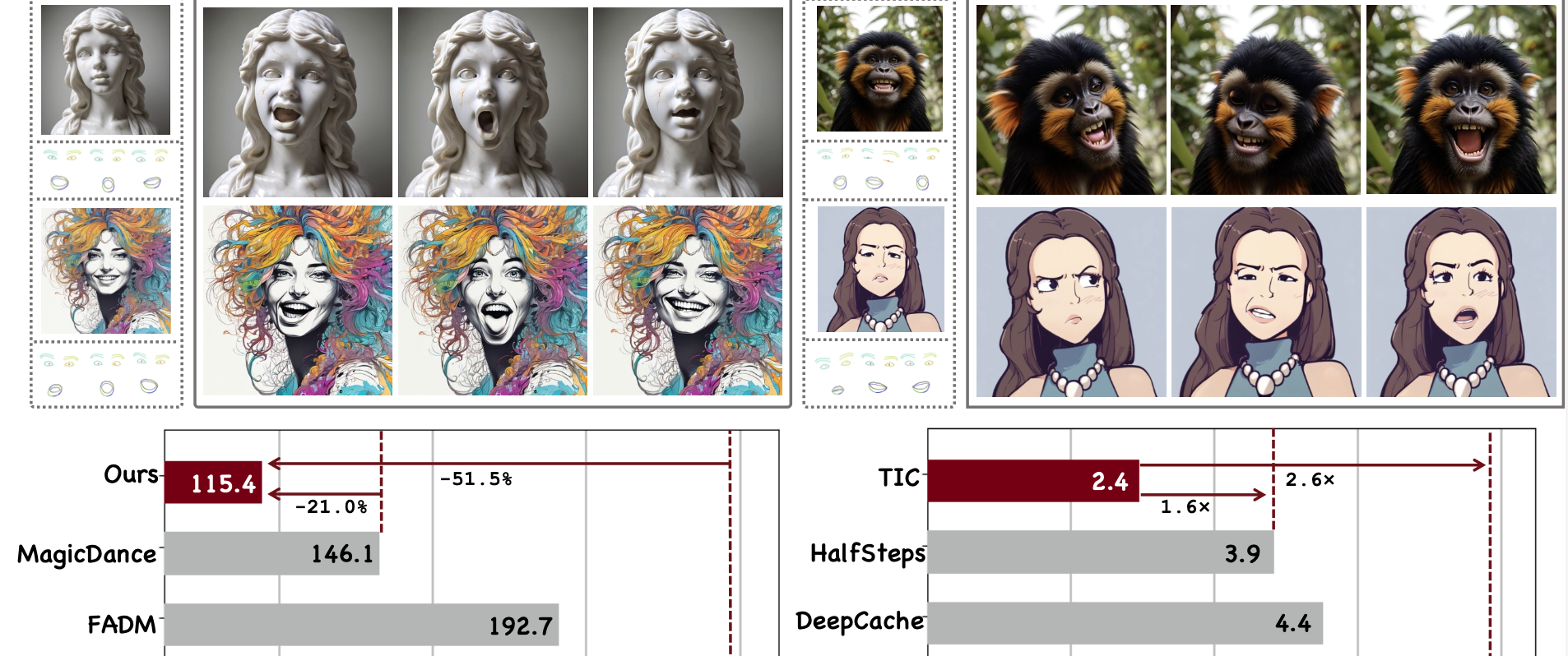
Follow-Your-Emoji-Faster: Towards Efficient, Fine-Controllable, and Expressive Freestyle Portrait AnimationYue Ma*, Zexuan Yan*, Hongyu Liu*, Hongfa Wang, Heng Pan, and 9 more authorsInternational Journal of Computer Vision (IJCV), 2025We present Follow-Your-Emoji-Faster, an efficient diffusion-based framework for freestyle portrait animation driven by facial landmarks; the main challenges in this task are preserving the identity of the reference portrait, accurately transferring target expressions, and maintaining long-term temporal consistency while ensuring generation efficiency; to address identity preservation and accurate expression retargeting, we enhance Stable Diffusion with two key components: expression-aware landmarks as explicit motion signals, which improve motion alignment, support exaggerated expressions, and reduce identity leakage, and a fine-grained facial loss that leverages both expression and facial masks to better capture subtle expressions and faithfully preserve the reference appearance; with these components, our model supports controllable and expressive animation across diverse portrait types, including real faces, cartoons, sculptures, and animals; however, diffusion-based frameworks typically struggle to efficiently generate long-term stable animation results, which remains a core challenge in this task; to address this, we propose a progressive generation strategy for stable long-term animation and introduce a Taylor-interpolated cache, achieving a 2.6× lossless acceleration; these two strategies ensure that our method produces high-quality results efficiently, making it user-friendly and accessible; finally, we introduce EmojiBench++, a more comprehensive benchmark comprising diverse portraits, driving videos, and landmark sequences; extensive evaluations on EmojiBench++ demonstrate that Follow-Your-Emoji-Faster achieves superior performance in both animation quality and controllability.
@article{ma2025followfaster, title = { Follow-Your-Emoji-Faster: Towards Efficient, Fine-Controllable, and Expressive Freestyle Portrait Animation}, author = {Ma, Yue and Yan, Zexuan and Liu, Hongyu and Wang, Hongfa and Pan, Heng and He, Yingqing and Yuan, Junkun and Zeng, Ailing and Cai, Chengfei and Shum, Heung-Yeung and Li, Zhifeng and Liu, Wei and linfeng, Zhang and Chen, Qifeng}, journal = {International Journal of Computer Vision (IJCV)}, year = {2025}, } - HeadArtist-VL: Vision / Language Guided 3D Head Generation with Self Score DistillationHongyu Liu, Xuan Wang, Ziyu Wan, Yujun Shen, Yibing Song, and 2 more authorsIEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI), 2025
We present HeadArtist-VL, a 3D head generation method that supports either vision or language input, utilizing a landmark-guided ControlNet as a generative prior and introducing a self-score distillation (SSD) pipeline that optimizes a parameterized 3D head model under the supervision of the prior itself, where given a sampled camera pose, an image and its landmarks are rendered from the head model, noised, and processed through a frozen ControlNet twice with different classifier-free guidance (CFG) weights to guide rendering alignment with language prompts, or for reference images, an image encoder extracts identity embeddings sent to the ControlNet, while a novel-view diffusion model synthesizes the reference image under the sampled pose to guide SSD, producing high-quality 3D head sculptures with rich geometry, photo-realistic appearance, and support for editing operations, significantly outperforming state-of-the-art methods.
-
 AvatarArtist: Open-Domain 4D AvatarizationHongyu Liu, Xuan Wang, Ziyu Wan, Yue Ma, Jingye Chen, and 4 more authorsProceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2025
AvatarArtist: Open-Domain 4D AvatarizationHongyu Liu, Xuan Wang, Ziyu Wan, Yue Ma, Jingye Chen, and 4 more authorsProceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2025This work focuses on open-domain 4D avatarization, with the purpose of creating a 4D avatar from a portrait image in an arbitrary style. We select parametric triplanes as the intermediate 4D representation and propose a practical training paradigm that takes advantage of both generative adversarial networks (GANs) and diffusion models. Our design stems from the observation that 4D GANs excel at bridging images and triplanes without supervision yet usually face challenges in handling diverse data distributions. A robust 2D diffusion prior emerges as the solution, assisting the GAN in transferring its expertise across various domains. The synergy between these experts permits the construction of a multi-domain image-triplane dataset, which drives the development of a general 4D avatar creator. Extensive experiments suggest that our model, AvatarArtist, is capable of producing high-quality 4D avatars with strong robustness to various source image domains. The code, the data, and the models will be made publicly available to facilitate future studies..
@article{liu2025avatarartist, title = {AvatarArtist: Open-Domain 4D Avatarization}, author = {Liu, Hongyu and Wang, Xuan and Wan, Ziyu and Ma, Yue and Chen, Jingye and Fan, Yanbo and Shen, Yujun and Song, Yibing and Chen, Qifeng}, journal = {Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)}, year = {2025}, }
2024
-
 Follow-Your-Emoji: Fine-Controllable and Expressive Freestyle Portrait AnimationYue Ma*, Hongyu Liu*, Hongfa Wang*, Heng Pan*, Yingqing He, and 6 more authorsACM Special Interest Group for Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques Asia (SIGGRAPH Asia), 2024
Follow-Your-Emoji: Fine-Controllable and Expressive Freestyle Portrait AnimationYue Ma*, Hongyu Liu*, Hongfa Wang*, Heng Pan*, Yingqing He, and 6 more authorsACM Special Interest Group for Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques Asia (SIGGRAPH Asia), 2024We present Follow-Your-Emoji, a diffusion-based framework for portrait animation that animates a reference portrait with target landmark sequences, addressing the challenges of preserving the identity of the reference portrait, transferring target expressions, and maintaining temporal consistency and fidelity by equipping the Stable Diffusion model with two key technologies: an explicit motion signal, namely expression-aware landmarks, to ensure accurate motion alignment, portray exaggerated expressions, and avoid identity leakage, and a facial fine-grained loss to enhance subtle expression perception and reference portrait reconstruction using expression and facial masks, achieving significant performance across diverse freestyle portraits (e.g., real humans, cartoons, sculptures, animals) with a progressive generation strategy for stable long-term animation, while introducing EmojiBench, a comprehensive benchmark of diverse portraits, driving videos, and landmarks, to verify its superiority through extensive evaluations.
@article{ma2024follow, title = {Follow-Your-Emoji: Fine-Controllable and Expressive Freestyle Portrait Animation}, author = {Ma, Yue and Liu, Hongyu and Wang, Hongfa and Pan, Heng and He, Yingqing and Yuan, Junkun and Zeng, Ailing and Cai, Chengfei and Shum, Heung-Yeung and Liu, Wei and Chen, Qifeng}, journal = {ACM Special Interest Group for Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques Asia (SIGGRAPH Asia)}, year = {2024}, } - LLMs Meet Multimodal Generation and Editing: A SurveyYingqing He*, Zhaoyang Liu*, Jingye Chen*, Zeyue Tian*, Hongyu Liu*, and 11 more authorsarXiv preprint arXiv:2405.19334, 2024
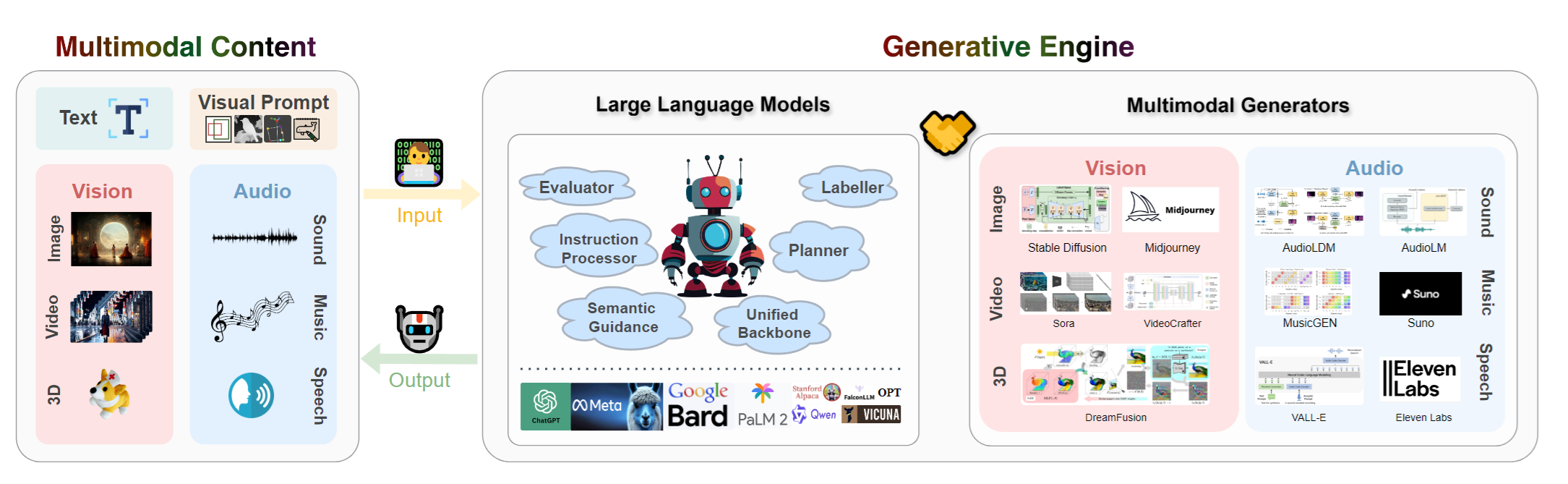
This survey includes works of image, video, 3D, and audio generation and editing. We emphasize the roles of LLMs on the generation and editing of these modalities. We also includes works of multimodal agents and generative AI safety.
@article{he2024llms, title = {LLMs Meet Multimodal Generation and Editing: A Survey}, author = {He, Yingqing and Liu, Zhaoyang and Chen, Jingye and Tian, Zeyue and Liu, Hongyu and Chi, Xiaowei and Liu, Runtao and Yuan, Ruibin and Xing, Yazhou and Wang, Wenhai and Dai, Jifeng and Zhang, Yong and Xue, Wei and Liu, Qifeng and Guo, Yike and Chen, Qifeng}, journal = {arXiv preprint arXiv:2405.19334}, year = {2024}, } -
 HeadArtist: Text-conditioned 3d head generation with self score distillationHongyu Liu, Xuan Wang, Ziyu Wan, Yujun Shen, Yibing Song, and 2 more authorsIn ACM Special Interest Group for Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques (SIGGRAPH), 2024
HeadArtist: Text-conditioned 3d head generation with self score distillationHongyu Liu, Xuan Wang, Ziyu Wan, Yujun Shen, Yibing Song, and 2 more authorsIn ACM Special Interest Group for Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques (SIGGRAPH), 2024This work presents HeadArtist for 3D head generation from text descriptions. With a landmark-guided ControlNet serving as the generative prior, we come up with an efficient pipeline that optimizes a parameterized 3D head model under the supervision of the prior distillation itself. We call such a process self score distillation (SSD). In detail, given a sampled camera pose, we first render an image and its corresponding landmarks from the head model, and add some particular level of noise onto the image. The noisy image, landmarks, and text condition are then fed into the frozen ControlNet twice for noise prediction. Two different classifier-free guidance (CFG) weights are applied during these two predictions, and the prediction difference offers a direction on how the rendered image can better match the text of interest. Experimental results suggest that our approach delivers high-quality 3D head sculptures with adequate geometry and photo-realistic appearance, significantly outperforming state-of-the-art methods. We also show that the same pipeline well supports editing the generated heads, including both geometry deformation and appearance change.
@inproceedings{liu2024headartist, title = {HeadArtist: Text-conditioned 3d head generation with self score distillation}, author = {Liu, Hongyu and Wang, Xuan and Wan, Ziyu and Shen, Yujun and Song, Yibing and Liao, Jing and Chen, Qifeng}, booktitle = {ACM Special Interest Group for Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques (SIGGRAPH)}, pages = {1--12}, year = {2024}, } -
 Cad: Photorealistic 3d generation via adversarial distillationZiyu Wan, Despoina Paschalidou, Ian Huang, Hongyu Liu, Bokui Shen, and 3 more authorsIn Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2024
Cad: Photorealistic 3d generation via adversarial distillationZiyu Wan, Despoina Paschalidou, Ian Huang, Hongyu Liu, Bokui Shen, and 3 more authorsIn Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2024The increased demand for 3D data in AR/VR, robotics and gaming applications, gave rise to powerful generative pipelines capable of synthesizing high-quality 3D objects. Most of these models rely on the Score Distillation Sampling (SDS) algorithm to optimize a 3D representation such that the rendered image maintains a high likelihood as evaluated by a pre-trained diffusion model. However, finding a correct mode in the high-dimensional distribution produced by the diffusion model is challenging and often leads to issues such as over-saturation, over-smoothing, and Janus-like artifacts. In this paper, we propose a novel learning paradigm for 3D synthesis that utilizes pre-trained diffusion models. Instead of focusing on mode-seeking, our method directly models the distribution discrepancy between multi-view renderings and diffusion priors in an adversarial manner, which unlocks the generation of high-fidelity and photorealistic 3D content, conditioned on a single image and prompt. Moreover, by harnessing the latent space of GANs and expressive diffusion model priors, our method facilitates a wide variety of 3D applications including single-view reconstruction, high diversity generation and continuous 3D interpolation in the open domain. The experiments demonstrate the superiority of our pipeline compared to previous works in terms of generation quality and diversity.
@inproceedings{wan2024cad, title = {Cad: Photorealistic 3d generation via adversarial distillation}, author = {Wan, Ziyu and Paschalidou, Despoina and Huang, Ian and Liu, Hongyu and Shen, Bokui and Xiang, Xiaoyu and Liao, Jing and Guibas, Leonidas}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition}, pages = {10194--10207}, year = {2024}, }
2023
-
 Make encoder great again in 3d gan inversion through geometry and occlusion-aware encodingZiyang Yuan*, Yiming Zhu*, Yu Li, Hongyu Liu, and Chun YuanIn Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, 2023
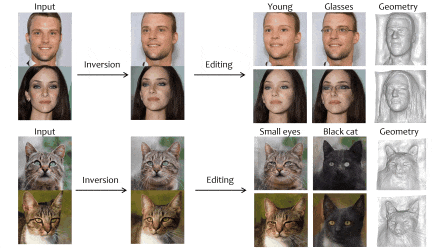
Make encoder great again in 3d gan inversion through geometry and occlusion-aware encodingZiyang Yuan*, Yiming Zhu*, Yu Li, Hongyu Liu, and Chun YuanIn Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, 20233D GAN inversion aims to achieve high reconstruction fidelity and reasonable 3D geometry simultaneously from a single image input. However, existing 3D GAN inversion methods rely on time-consuming optimization for each individual case. In this work, we introduce a novel encoder-based inversion framework based on EG3D, one of the most widely-used 3D GAN models. We leverage the inherent properties of EG3D’s latent space to design a discriminator and a background depth regularization. This enables us to train a geometry-aware encoder capable of converting the input image into corresponding latent code. Additionally, we explore the feature space of EG3D and develop an adaptive refinement stage that improves the representation ability of features in EG3D to enhance the recovery of fine-grained textural details. Finally, we propose an occlusion-aware fusion operation to prevent distortion in unobserved regions. Our method achieves impressive results comparable to optimization-based methods while operating up to 500 times faster. Our framework is well-suited for applications such as semantic editing.
@inproceedings{yuan2023make, title = {Make encoder great again in 3d gan inversion through geometry and occlusion-aware encoding}, author = {Yuan, Ziyang and Zhu, Yiming and Li, Yu and Liu, Hongyu and Yuan, Chun}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision}, pages = {2437--2447}, year = {2023}, } -
 XFormer: fast and accurate monocular 3D body captureLihui Qian*, Xintong Han*, Faqiang Wang, Hongyu Liu, Haoye Dong, and 4 more authorsarXiv preprint arXiv:2305.11101, 2023
XFormer: fast and accurate monocular 3D body captureLihui Qian*, Xintong Han*, Faqiang Wang, Hongyu Liu, Haoye Dong, and 4 more authorsarXiv preprint arXiv:2305.11101, 2023We present XFormer, a novel human mesh and motion capture method that achieves real-time performance on consumer CPUs using only monocular images as input. The proposed network architecture consists of two branches: a keypoint branch that estimates 3D human mesh vertices from 2D keypoints, and an image branch that directly predicts from RGB image features. At the core of our method is a cross-modal transformer block, which facilitates information flow between the two branches by modeling the attention between 2D keypoint coordinates and image spatial features. Our architecture is carefully designed to enable training on diverse datasets, including images with 2D/3D annotations, images with 3D pseudo labels, and motion capture datasets without associated images. This design significantly enhances the accuracy and generalization ability of our system. Built on a lightweight backbone (MobileNetV3), our method achieves blazing-fast performance, running at over 30fps on a single CPU core, while maintaining competitive accuracy. Additionally, with an HRNet backbone, XFormer achieves state-of-the-art performance on the Human3.6 and 3DPW datasets.
@article{qian2023xformer, title = {XFormer: fast and accurate monocular 3D body capture}, author = {Qian, Lihui and Han, Xintong and Wang, Faqiang and Liu, Hongyu and Dong, Haoye and Li, Zhiwen and Wei, Huawei and Lin, Zhe and Jin, Cheng-Bin}, journal = {arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.11101}, year = {2023}, } -
 Delving stylegan inversion for image editing: A foundation latent space viewpointHongyu Liu, Yibing Song, and Qifeng ChenIn Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), 2023
Delving stylegan inversion for image editing: A foundation latent space viewpointHongyu Liu, Yibing Song, and Qifeng ChenIn Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), 2023GAN inversion and editing via StyleGAN maps an input image into the embedding spaces (W, W+, and F) to simultaneously maintain image fidelity and meaningful manipulation. From latent space W to extended latent space W+ to feature space F in StyleGAN, the editability of GAN inversion decreases while its reconstruction quality increases. Recent GAN inversion methods typically explore W+ and F rather than W to improve reconstruction fidelity while maintaining editability. As W+ and F are derived from W that is essentially the foundation latent space of StyleGAN, these GAN inversion methods focusing on W+ and F spaces could be improved by stepping back to W. In this work, we propose to first obtain the precise latent code in foundation latent space W. We introduce contrastive learning to align W and the image space for precise latent code discovery. %The obtaining process is by using contrastive learning to align W and the image space. Then, we leverage a cross-attention encoder to transform the obtained latent code in W into W+ and F, accordingly. Our experiments show that our exploration of the foundation latent space W improves the representation ability of latent codes in W+ and features in F, which yields state-of-the-art reconstruction fidelity and editability results on the standard benchmarks.
@inproceedings{liu2023delving, title = {Delving stylegan inversion for image editing: A foundation latent space viewpoint}, author = {Liu, Hongyu and Song, Yibing and Chen, Qifeng}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR)}, pages = {10072--10082}, year = {2023}, } -
 Human motionformer: Transferring human motions with vision transformersHongyu Liu*, Xintong Han*, Chengbin Jin, Lihui Qian, Huawei Wei, and 6 more authorsInternational Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR) , 2023
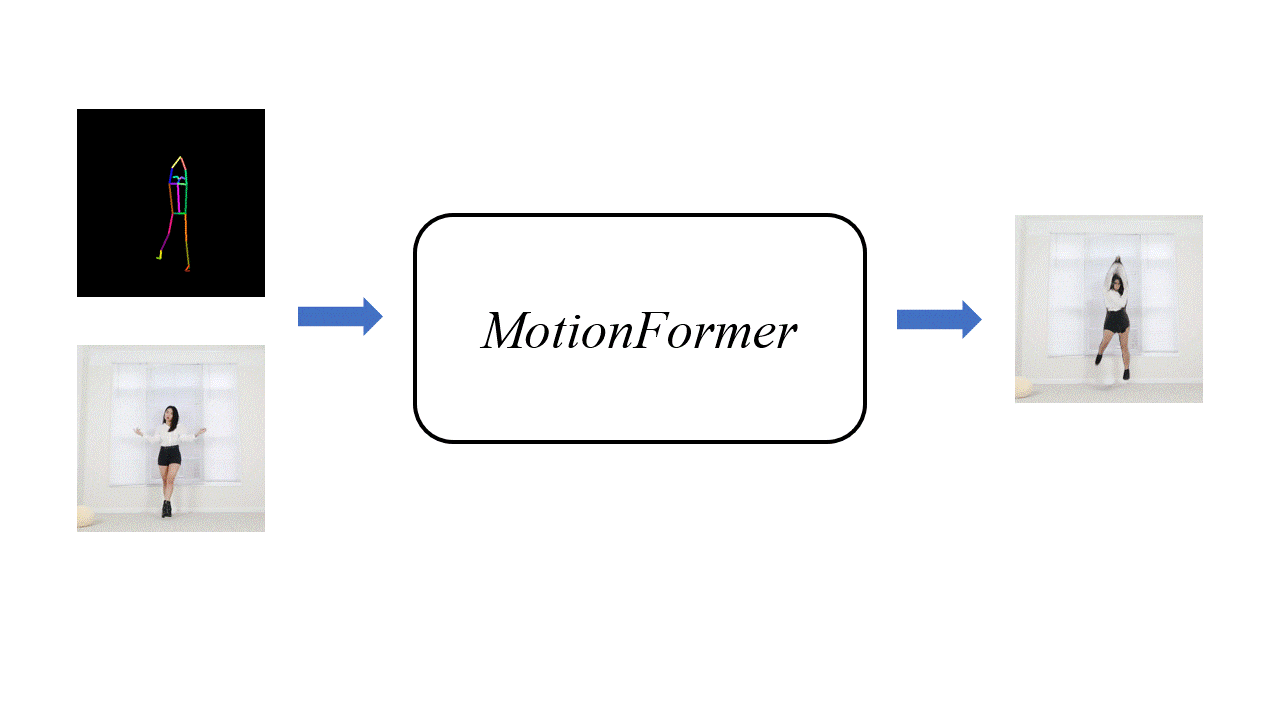
Human motionformer: Transferring human motions with vision transformersHongyu Liu*, Xintong Han*, Chengbin Jin, Lihui Qian, Huawei Wei, and 6 more authorsInternational Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR) , 2023Human motion transfer aims to transfer motions from a target dynamic person to a source static one for motion synthesis. An accurate matching between the source person and the target motion in both large and subtle motion changes is vital for improving the transferred motion quality. In this paper, we propose Human MotionFormer, a hierarchical ViT framework that leverages global and local perceptions to capture large and subtle motion matching, respectively. It consists of two ViT encoders to extract input features (i.e., a target motion image and a source human image) and a ViT decoder with several cascaded blocks for feature matching and motion transfer. In each block, we set the target motion feature as Query and the source person as Key and Value, calculating the cross-attention maps to conduct a global feature matching. Further, we introduce a convolutional layer to improve the local perception after the global cross-attention computations. This matching process is implemented in both warping and generation branches to guide the motion transfer. During training, we propose a mutual learning loss to enable the co-supervision between warping and generation branches for better motion representations. Experiments show that our Human MotionFormer sets the new state-of-the-art performance both qualitatively and quantitatively.
@article{liu2023human, title = {Human motionformer: Transferring human motions with vision transformers}, author = {Liu, Hongyu and Han, Xintong and Jin, Chengbin and Qian, Lihui and Wei, Huawei and Lin, Zhe and Wang, Faqiang and Dong, Haoye and Song, Yibing and Xu, Jia and others}, journal = {International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR) }, year = {2023}, }
2022
- Spotlight
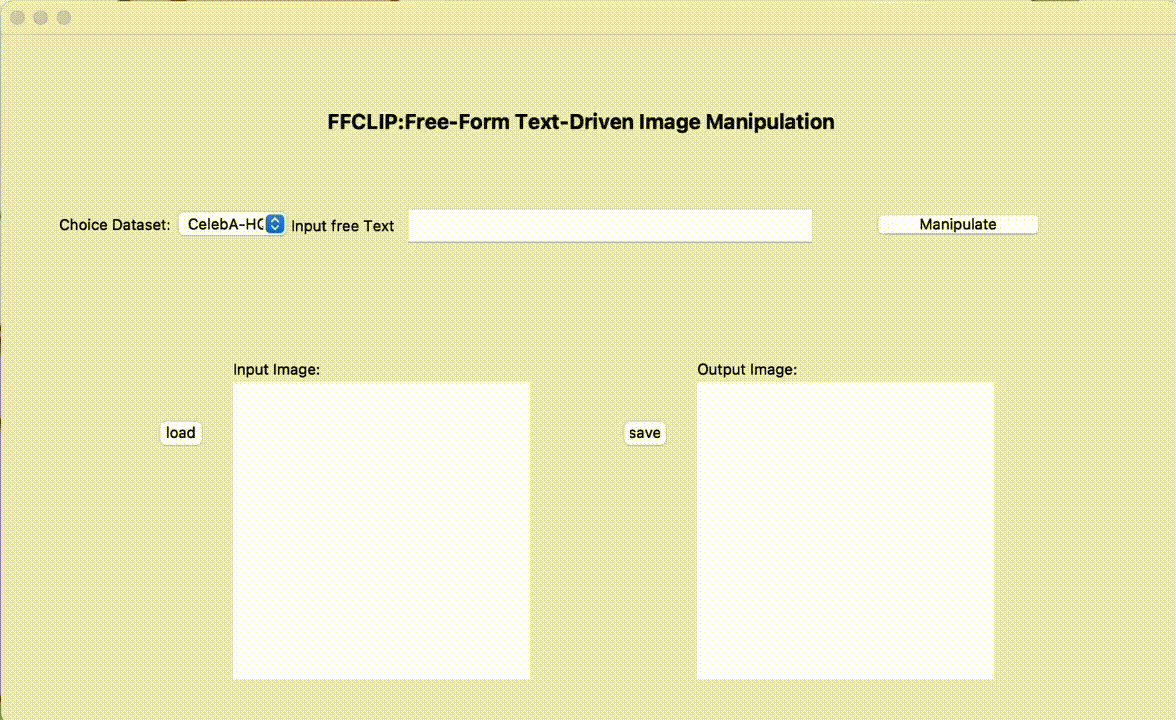 One model to edit them all: Free-form text-driven image manipulation with semantic modulationsYiming Zhu*, Hongyu Liu*, Yibing Song, Ziyang Yuan, Xintong Han, and 3 more authorsAdvances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeuralIPS), 2022
One model to edit them all: Free-form text-driven image manipulation with semantic modulationsYiming Zhu*, Hongyu Liu*, Yibing Song, Ziyang Yuan, Xintong Han, and 3 more authorsAdvances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeuralIPS), 2022Free-form text prompts allow users to describe their intentions during image manipulation conveniently. Based on the visual latent space of StyleGAN[21] and text embedding space of CLIP[34], studies focus on how to map these two latent spaces for text-driven attribute manipulations. Currently, the latent mapping between these two spaces is empirically designed and confines that each manipulation model can only handle one fixed text prompt. In this paper, we propose a method named Free-Form CLIP (FFCLIP), aiming to establish an automatic latent mapping so that one manipulation model handles free-form text prompts. Our FFCLIP has a cross-modality semantic modulation module containing semantic alignment and injection. The semantic alignment performs the automatic latent mapping via linear transformations with a cross attention mechanism. After alignment, we inject semantics from text prompt embeddings to the StyleGAN latent space. For one type of image (e.g., ’human portrait’), one FFCLIP model can be learned to handle free-form text prompts. Meanwhile, we observe that although each training text prompt only contains a single semantic meaning, FFCLIP can leverage text prompts with multiple semantic meanings for image manipulation. In the experiments, we evaluate FFCLIP on three types of images (i.e., ’human portraits’, ’cars’, and ’churches’). Both visual and numerical results show that FFCLIP effectively produces semantically accurate and visually realistic images.
@article{zhu2022one, title = {One model to edit them all: Free-form text-driven image manipulation with semantic modulations}, author = {Zhu, Yiming and Liu, Hongyu and Song, Yibing and Yuan, Ziyang and Han, Xintong and Yuan, Chun and Chen, Qifeng and Wang, Jue}, journal = {Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeuralIPS)}, volume = {35}, pages = {25146--25159}, year = {2022}, }
2021
-
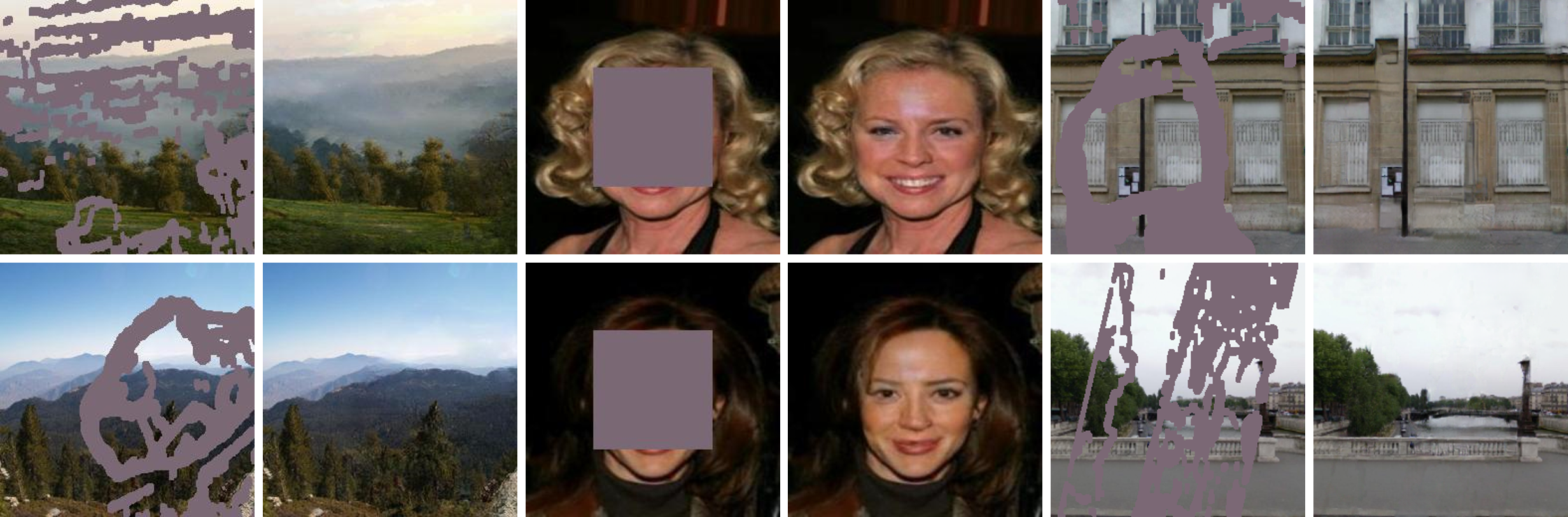
 Pd-gan: Probabilistic diverse gan for image inpaintingHongyu Liu, Ziyu Wan, Wei Huang, Yibing Song, Xintong Han, and 1 more authorIn Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), 2021
Pd-gan: Probabilistic diverse gan for image inpaintingHongyu Liu, Ziyu Wan, Wei Huang, Yibing Song, Xintong Han, and 1 more authorIn Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), 2021We propose PD-GAN, a probabilistic diverse GAN for image inpainting. Given an input image with arbitrary hole regions, PD-GAN produces multiple inpainting results with diverse and visually realistic content. Our PD-GAN is built upon a vanilla GAN which generates images based on random noise. During image generation, we modulate deep features of input random noise from coarse-to-fine by injecting an initially restored image and the hole regions in multiple scales. We argue that during hole filling, the pixels near the hole boundary should be more deterministic (i.e., with higher probability trusting the context and initially restored image to create natural inpainting boundary), while those pixels lying in the center of the hole should enjoy more degrees of freedom (i.e., more likely to depend on the random noise for enhancing diversity). To this end, we propose spatially probabilistic diversity normalization (SPDNorm) inside the modulation to model the probability of generating a pixel conditioned on the context information. SPDNorm dynamically balances the realism and diversity inside the hole region, making the generated content more diverse towards the hole center and resemble neighboring image content more towards the hole boundary. Meanwhile, we propose a perceptual diversity loss to further empower PD-GAN for diverse content generation. Experiments on benchmark datasets including CelebA-HQ, Places2, and Paris Street View indicate that PD-GAN is effective for diverse and visually realistic image restoration.
@inproceedings{liu2021pd, title = {Pd-gan: Probabilistic diverse gan for image inpainting}, author = {Liu, Hongyu and Wan, Ziyu and Huang, Wei and Song, Yibing and Han, Xintong and Liao, Jing}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR)}, pages = {9371--9381}, year = {2021}, } -
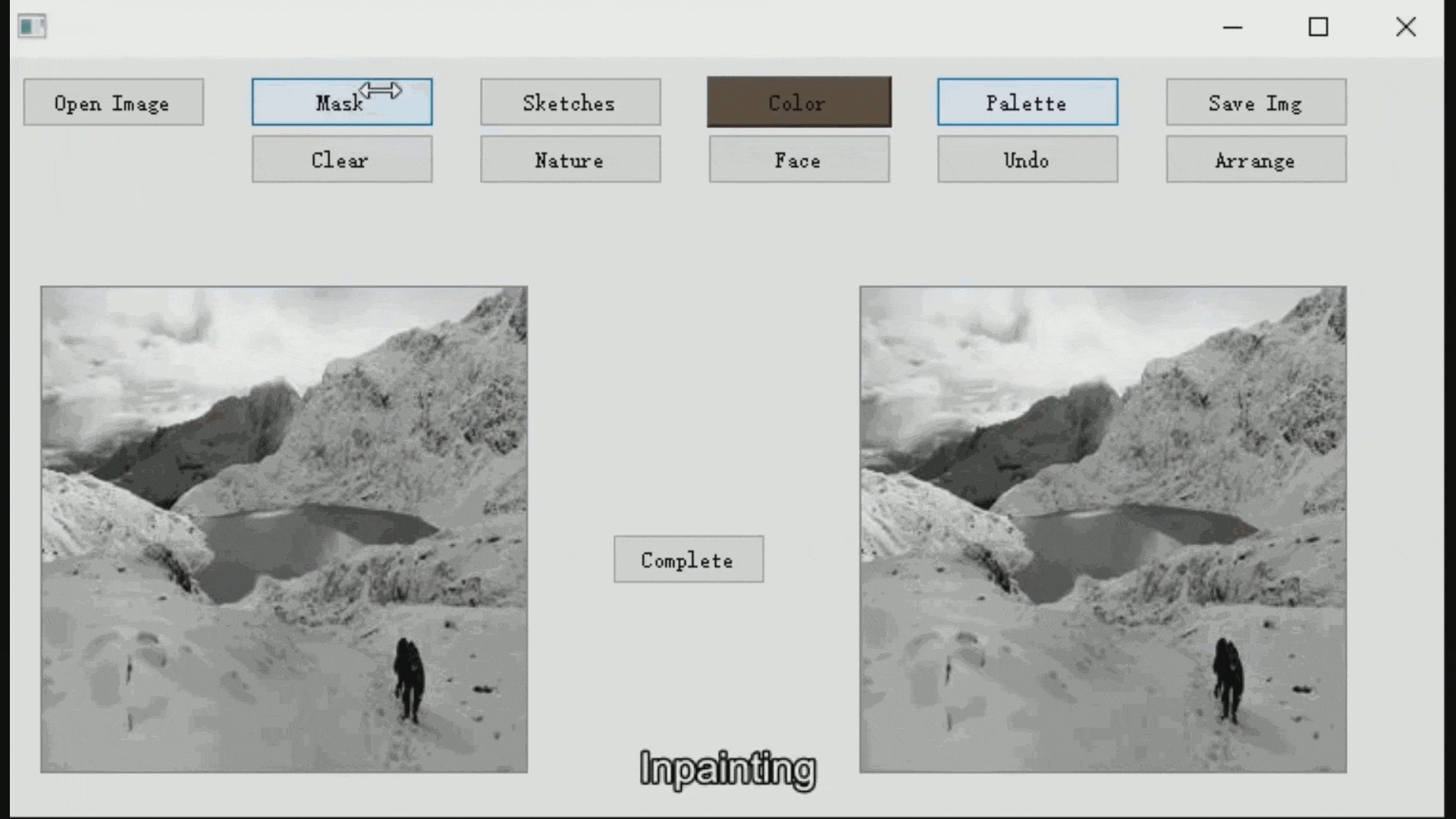 Deflocnet: Deep image editing via flexible low-level controlsHongyu Liu, Ziyu Wan, Wei Huang, Yibing Song, Xintong Han, and 3 more authorsIn Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2021
Deflocnet: Deep image editing via flexible low-level controlsHongyu Liu, Ziyu Wan, Wei Huang, Yibing Song, Xintong Han, and 3 more authorsIn Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2021User-intended visual content fills the hole regions of an input image in the image editing scenario. The coarse low-level inputs, which typically consist of sparse sketch lines and color dots, convey user intentions for content creation (i.e., free-form editing). While existing methods combine an input image and these low-level controls for CNN inputs, the corresponding feature representations are not sufficient to convey user intentions, leading to unfaithfully generated content. In this paper, we propose DeFLOCNet which relies on a deep encoder-decoder CNN to retain the guidance of these controls in the deep feature representations. In each skip-connection layer, we design a structure generation block. Instead of attaching low-level controls to an input image, we inject these controls directly into each structure generation block for sketch line refinement and color propagation in the CNN feature space. We then concatenate the modulated features with the original decoder features for structure generation. Meanwhile, DeFLOCNet involves another decoder branch for texture generation and detail enhancement. Both structures and textures are rendered in the decoder, leading to user-intended editing results. Experiments on benchmarks demonstrate that DeFLOCNet effectively transforms different user intentions to create visually pleasing content.
@inproceedings{liu2021deflocnet, title = {Deflocnet: Deep image editing via flexible low-level controls}, author = {Liu, Hongyu and Wan, Ziyu and Huang, Wei and Song, Yibing and Han, Xintong and Liao, Jing and Jiang, Bin and Liu, Wei}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)}, pages = {10765--10774}, year = {2021}, }
2020
- Oral
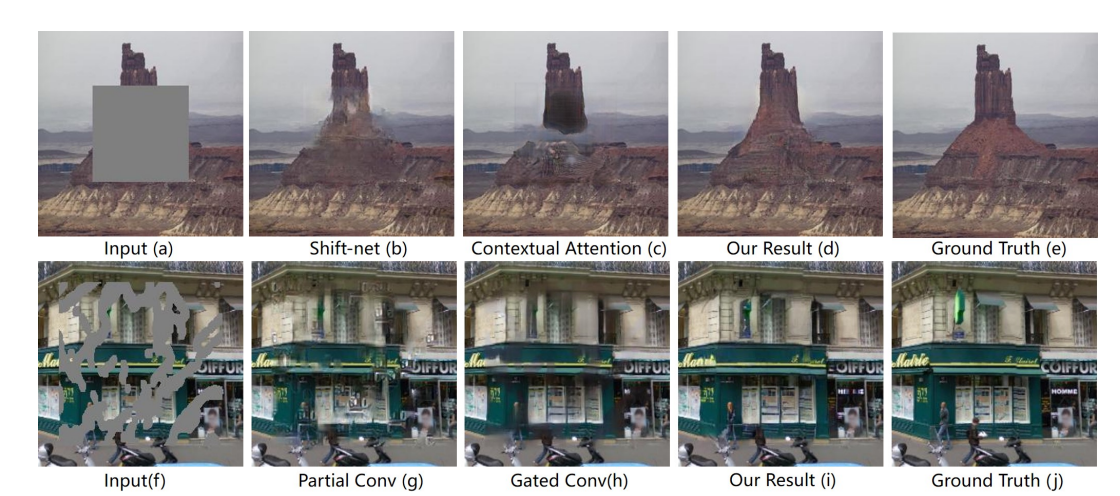
 Rethinking image inpainting via a mutual encoder-decoder with feature equalizationsHongyu Liu, Bin Jiang, Yibing Song, Wei Huang, and Chao YangIn Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, August 23–28, 2020, Proceedings, Part II 16 (ECCV), 2020
Rethinking image inpainting via a mutual encoder-decoder with feature equalizationsHongyu Liu, Bin Jiang, Yibing Song, Wei Huang, and Chao YangIn Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, August 23–28, 2020, Proceedings, Part II 16 (ECCV), 2020Deep encoder-decoder based CNNs have advanced image inpainting methods for hole filling. While existing methods recover structures and textures step-by-step in the hole regions, they typically use two encoder-decoders for separate recovery. The CNN features of each encoder are learned to capture either missing structures or textures without considering them as a whole. The insufficient utilization of these encoder features hampers the performance of recovering both structures and textures. In this paper, we propose a mutual encoder-decoder CNN for joint recovery of both. We use CNN features from the deep and shallow layers of the encoder to represent structures and textures of an input image, respectively. The deep layer features are sent to a structure branch, while the shallow layer features are sent to a texture branch. In each branch, we fill holes in multiple scales of the CNN features. The filled CNN features from both branches are concatenated and then equalized. During feature equalization, we reweigh channel attentions first and propose a bilateral propagation activation function to enable spatial equalization. To this end, the filled CNN features of structure and texture mutually benefit each other to represent image content at all feature levels. We then use the equalized feature to supplement decoder features for output image generation through skip connections. Experiments on benchmark datasets show that the proposed method is effective to recover structures and textures and performs favorably against state-of-the-art approaches.
@inproceedings{liu2020rethinking, title = {Rethinking image inpainting via a mutual encoder-decoder with feature equalizations}, author = {Liu, Hongyu and Jiang, Bin and Song, Yibing and Huang, Wei and Yang, Chao}, booktitle = {Computer Vision--ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, August 23--28, 2020, Proceedings, Part II 16 (ECCV)}, pages = {725--741}, year = {2020}, organization = {Springer}, }
2019
-
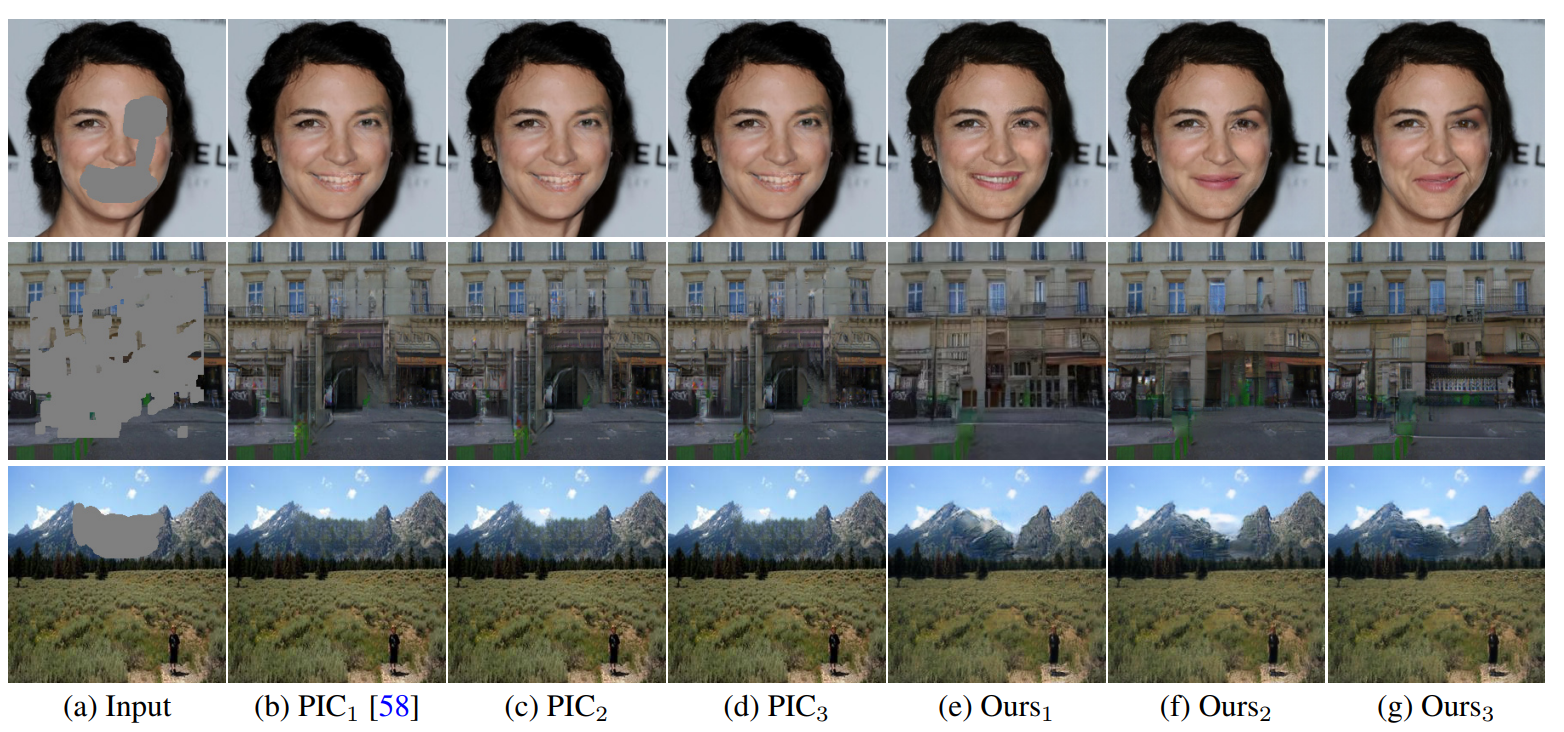
 Coherent Semantic Attention for Image InpaintingHongyu Liu, Bin Jiang, Yi Xiao, and Chao YangIn Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Oct 2019
Coherent Semantic Attention for Image InpaintingHongyu Liu, Bin Jiang, Yi Xiao, and Chao YangIn Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Oct 2019The latest deep learning-based approaches have shown promising results for the challenging task of inpainting missing regions of an image. However, the existing methods often generate contents with blurry textures and distorted structures due to the discontinuity of the local pixels. From a semantic-level perspective, the local pixel discontinuity is mainly because these methods ignore the semantic relevance and feature continuity of hole regions. To handle this problem, we investigate the human behavior in repairing pictures and propose a fined deep generative model-based approach with a novel coherent semantic attention (CSA) layer, which can not only preserve contextual structure but also make more effective predictions of missing parts by modeling the semantic relevance between the holes features. The task is divided into rough, refinement as two steps and we model each step with a neural network under the U-Net architecture, where the CSA layer is embedded into the encoder of refinement step. Meanwhile, we further propose consistency loss and feature patch discriminator to stabilize the network training process and improve the details. The experiments on CelebA, Places2, and Paris StreetView datasets have validated the effectiveness of our proposed methods in image inpainting tasks and can obtain images with a higher quality as compared with the existing stateof-the-art approaches
@inproceedings{Liu_2019_ICCV, author = {Liu, Hongyu and Jiang, Bin and Xiao, Yi and Yang, Chao}, title = {Coherent Semantic Attention for Image Inpainting}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV)}, month = oct, year = {2019}, }